Al (Träd)
Beskrivning
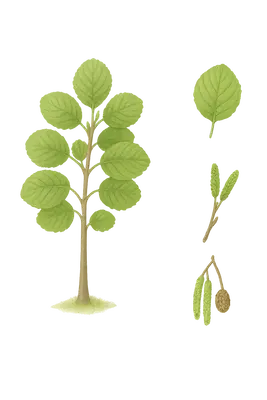
Alar (Alnus-arter) är lövfällande träd eller buskar i björkfamiljen (Betulaceae). De växer ofta vid sjöar, vattendrag, våtmarker och fuktiga skogsområden, där de fixerar kväve i marken. Alar känns igen på sina hängande hanhängen och små, upprättstående honkottar. De släpper stora mängder pollen under sen vinter och tidig vår innan löven slagit ut. Vanliga arter i Sverige är klibbal (Alnus glutinosa) och gråal (Alnus incana).
Allergisymptom
Alpollen ger tidiga vårsymptom:
- Nysningar och rinnande eller täppt näsa
- Kliande, rinnande och röda ögon
- Hosta och halsirritation
- Försämrad astma och pipande andning
Personer allergiska mot alpollen reagerar ofta på björkpollen också eftersom de delar allergena proteiner. Oralt Allergisyndrom (OAS) är vanligt – du kan få klåda eller stickningar i mun och svalg av råa äpplen, päron, körsbär, persikor, hasselnötter och mandlar. Tillagning hjälper oftast.
Typisk pollensäsong
Alpollensäsongen börjar i sen vinter till tidig vår:
- Södra och mellersta Sverige: Februari-mars med topp i mars-april
- Norra Sverige: Kan börja något senare
- Mildare vintrar leder ofta till tidigare pollensäsong
Geografisk utbredning
Alar växer över hela norra halvklotet:
- Sverige: Klibbal är vanligast i södra och mellersta Sverige nära vatten. Gråal är utbredd över hela landet, särskilt i norr.
- Europa: Vanlig i fuktiga områden
- Nordamerika: USA och Kanada
- Asien: Tempererade regioner
Tips för pollenallergiker
- Kolla pollenprognoser – alsäsongen börjar tidigt, ofta redan i februari
- Håll fönster stängda och använd luftrenare med HEPA-filter
- Duscha och byt kläder efter utomhusvistelse
- Antihistaminer och nässpray med kortison kan hjälpa – prata med din läkare
- Om du reagerar på al, förvänta dig reaktioner på björk också
- Vid svåra besvär, överväg allergitest eller immunterapi