Alder (Tree)
Description
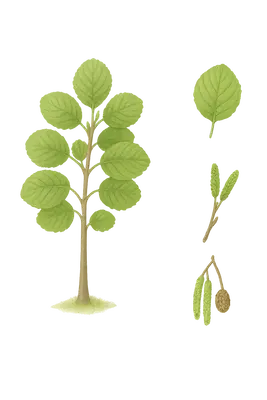
Alder trees (Alnus species) are deciduous trees or large shrubs in the birch family (Betulaceae). They typically grow near rivers, wetlands, and damp woodlands, where they help fix nitrogen in the soil. You can recognize alders by their drooping male catkins and small, persistent woody female cones. They release abundant pollen in late winter and early spring, often before their leaves emerge. Common species include black alder (Alnus glutinosa) in Europe and red alder (Alnus rubra) in North America.
Allergy Symptoms
Alder pollen triggers early spring allergies with typical symptoms:
- Sneezing and runny or congested nose
- Itchy, watery, red eyes
- Coughing and throat irritation
- Asthma flare-ups and wheezing
People allergic to alder often also react to birch pollen because of shared allergens. Oral Allergy Syndrome (OAS) is common too — you might get itching or tingling in your mouth and throat from raw apples, pears, cherries, peaches, hazelnuts, and almonds. Cooking these foods usually helps.
Typical Pollination Period
Alder pollen season starts in late winter, typically January to March, with peak levels around February to March in temperate regions. Alder is one of the first trees to pollinate each year, often marking the start of tree pollen season. Timing varies with climate — earlier in mild coastal areas, later inland where it’s colder.
Geographic Distribution
Alder trees grow widely across the Northern Hemisphere:
- Europe: Common throughout, especially in wet lowland areas and along streams and rivers
- North America: Most common in the Pacific Northwest (Alaska to California) and in eastern regions
- Asia: Found in parts of Russia, Japan, and other temperate areas
Tips for Allergy Sufferers
- Check local pollen forecasts — alder season starts earlier than most people expect
- Keep windows closed and use HEPA air purifiers indoors
- Shower and change clothes after being outside
- Antihistamines or nasal corticosteroids can help — talk to your doctor
- Watch out for cross-reactive foods if you get Oral Allergy Syndrome
- For persistent symptoms, consider allergy testing or immunotherapy